Sulfasalazine
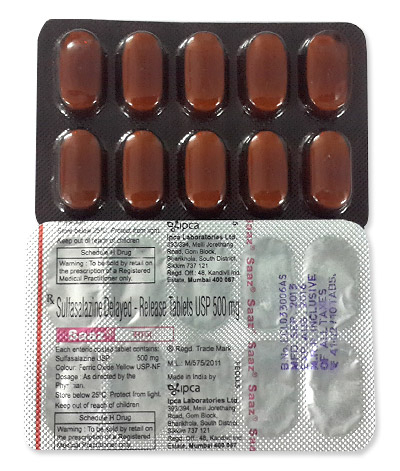
Sulfasalazine
- Sulfasalazine can be purchased in pharmacies without a prescription, with delivery available throughout the United Kingdom.
- Sulfasalazine is used to treat ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis. It acts as an anti-inflammatory agent in the intestines.
- The usual dosage of sulfasalazine for adults is 2–4 g per day, divided into multiple doses.
- The form of administration is in tablet form (500 mg).
- The onset time of sulfasalazine’s effects typically begins within 3–6 weeks for full response.
- The duration of action is long-term, as clinically indicated for chronic conditions.
- Alcohol should be avoided while taking sulfasalazine.
- The most common side effect is headache.
- Would you like to try sulfasalazine without a prescription?
Sulfasalazine
Basic Sulfasalazine Information
- INN (International Nonproprietary Name): Sulfasalazine
- Brand names available in United Kingdom: Salazopyrin, Azulfidine, Salazopyrin EN
- ATC Code: A07EC01
- Forms & dosages: Tablets 500 mg and 250 mg, extended-release formulations
- Manufacturers in United Kingdom: Pfizer, ratiopharm, and various others
- Registration status in United Kingdom: Prescription only
- OTC / Rx classification: Prescription Only
Everyday Use & Best Practices
When it comes to the effective use of sulfasalazine, understanding the day-to-day application and best practices can greatly enhance adherence and efficacy. Many patients find that aligning their medication routine with daily activities maximises the benefits.
Morning vs Evening Dosing
As with many medications, the timing of sulfasalazine doses can influence both efficacy and tolerability. Taking sulfasalazine in the morning can help to integrate it into the patient's routine, especially alongside breakfast—a common habit in the UK. For those who take multiple medications, establishing a consistent routine in the morning or evening can support better adherence. Aligning taken doses with daily routines, such as having it with breakfast or dinner, can contribute to a more reliable treatment outcome.
Taking With or Without Meals (UK Diet Habits)
It is essential to take sulfasalazine with food to improve absorption and mitigate potential gastrointestinal discomfort. Many traditional UK meals provide an excellent opportunity for dosing, whether it's at breakfast, lunch, or dinner. The richness of typical diets, often involving starchy foods, proteins, or vegetables, can create a suitable environment for the enhanced absorption of the medication. Patients should, therefore, be encouraged to have sulfasalazine at mealtimes to help maximise its effectiveness and reduce side effects.
Safety Priorities
While sulfasalazine is effective for various conditions, prioritising safety when using this medication is crucial. Certain populations may need to avoid use or be cautious when taking it.
Who Should Avoid It (MHRA Warnings)
Based on guidance from the MHRA, there are several contraindications for sulfasalazine:
- Hypersensitivity to sulfasalazine or similar compounds
- Severe renal impairment
- History of porphyria
Activities to Limit (Driving, Work Safety)
Certain side effects associated with sulfasalazine may impair motor skills and cognitive function. Patients experiencing dizziness or drowsiness are advised to avoid activities that require full attention, such as driving or operating machinery. At work, any responsibilities involving heavy machinery should be approached with caution. It is essential to monitor how the medication affects individual abilities and adjust activities accordingly.
Dosage & Adjustments
Appropriately prescribing sulfasalazine entails understanding its dosage and necessary adjustments for specific populations. This ensures effective management of conditions while minimising risks.
General Regimen (NHS Guidance)
The standard dosages for sulfasalazine reflect its application in treating conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis:
| Indication | Adult Dosage |
|---|---|
| Ulcerative colitis (active) | 2–4 g/day, divided into two to four doses |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Start: 500 mg/day; increase to 2–3 g/day in divided doses |
Special Cases (Elderly, Comorbidities)
When prescribing sulfasalazine for older patients or those with pre-existing conditions, a cautious approach is essential. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for individuals with liver or kidney impairment. Starting at a lower dose and titrating up allows for monitoring of side effects or adverse reactions. Caregivers should be adequately informed to assist in administering the medication correctly.
User Testimonials
Feedback from patients often provides insight into the effectiveness of medications like sulfasalazine. A wealth of anecdotal evidence exists that can be particularly useful for new users considering this treatment.
Positive Reports From UK Patients
On various patient forums, many have shared their journeys using sulfasalazine, reporting effective treatment outcomes. Patients have noted significant improvements in their symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis. Satisfaction often stems from the medication's ability to reduce flare-ups and maintain remission, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Common Challenges (Patient.info, NHS Forums)
However, it's not uncommon for some users to encounter challenges when taking sulfasalazine. Side effects such as headaches, nausea, and abdominal discomfort have been reported. Patients on NHS forums have offered practical tips for managing these concerns, such as adjusting the timing of doses and ensuring adequate hydration. Addressing these challenges head-on can be equally important as the medication itself in optimising treatment outcomes.
Buying Guide
When considering the purchase of sulfasalazine, understanding where it can be accessed and the associated costs is critical for patients.
Pharmacy Sources (Boots, LloydsPharmacy, Superdrug)
In the UK, sulfasalazine can be obtained from major pharmacy chains including Boots, LloydsPharmacy, and Superdrug. Each of these pharmacies plays a vital role in ensuring patients have access to their prescribed medications. Many of these pharmacies also offer consulting services that can provide additional information and reassurance, assisting patients in their treatment journey.
Price Comparison (NHS Prescription Charge vs Private)
Patients need to consider the cost of obtaining sulfasalazine, as it may vary depending on whether it’s purchased privately or through the NHS. Those eligible for NHS prescriptions might pay a nominal fee but can also benefit from exemptions based on specific criteria. Understanding these costs is essential to prevent financial strain while accessing needed medications.
What’s Inside & How It Works
Ingredients overview
Sulfasalazine, known by various brand names including Salazopyrin and Azulfidine, contains active and inactive ingredients that work in harmony to manage inflammation. The primary active ingredient, sulfasalazine itself, is combined with inactive components such as fillers, binders, and stabilizers necessary for tablet formulation. Typically, sulfasalazine tablets come in 500 mg dosages, suitable for oral administration. While the formulation may vary across different brands, such as the extended-release version Salazopyrin EN, the core ingredient remains the same, ensuring the intended therapeutic efficacy for conditions like ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Mechanism basics explained simply
Sulfasalazine acts as an anti-inflammatory medication primarily through its metabolite, 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA). This compound works by reducing inflammation in the gut lining, which is crucial for patients suffering from ulcerative colitis. It inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators, helping to alleviate symptoms like pain and diarrhoea. Furthermore, sulfasalazine suppresses the immune response responsible for joint inflammation in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, thereby providing relief to those impacted. This dual-action approach makes it a staple in managing chronic inflammatory disorders.
Main Indications
Approved uses
In the UK, sulfasalazine is primarily approved for use in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis, as per the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). For ulcerative colitis, it’s often prescribed to manage active phases of the disease, facilitating symptoms relief and promoting remission. In rheumatoid arthritis, sulfasalazine is used as a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) that helps reduce joint inflammation and damage. Both of these applications underline its significance in chronic inflammatory conditions where effective management is essential.
Off-label uses in UK clinics
While sulfasalazine is chiefly prescribed for ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis, some clinicians in the UK have begun to explore off-label uses. Notably, it has shown effectiveness in managing other autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and ankylosing spondylitis. Additionally, its potential benefits in treating certain skin disorders like psoriasis have been observed, although these uses are less common. Off-label prescriptions reflect clinicians' attempts to leverage sulfasalazine's anti-inflammatory properties for broader patient benefit, although such approaches should be carefully monitored.
Interaction Warnings
Food interactions
When taking sulfasalazine, dietary considerations are crucial. Alcohol consumption can exacerbate the risk of side effects, including gastrointestinal upset and potential liver toxicity. As such, limiting or avoiding alcohol while on sulfasalazine is advisable. Furthermore, beverages like tea and coffee may interfere with the absorption of the medication, potentially reducing its efficacy. Patients are encouraged to maintain a balanced diet and consult with healthcare providers about any specific dietary restrictions when initiating treatment with sulfasalazine.
Drug conflicts
Sulfasalazine is known to interact with various medications. Reports on the MHRA’s Yellow Card system highlight potential conflicts with drugs such as warfarin, leading to increased bleeding risks, and methotrexate, where the combination can heighten the risk of liver toxicity. Patients are advised to thoroughly discuss their current medication regimens with healthcare providers before starting sulfasalazine. This precaution ensures that clinicians can assess and manage any potential drug interactions that may impact the treatment outcomes.
Latest Evidence & Insights
Key UK & EU studies 2022–2025
Recent studies from the UK and EU have delved into the effectiveness and safety of sulfasalazine for various conditions. Preliminary findings suggest that sulfasalazine maintains its efficacy in managing ulcerative colitis, with studies confirming sustained remission rates in patients. Furthermore, ongoing trials are examining its long-term effects on joint health in rheumatoid arthritis patients, indicating promising results regarding its safety profile. These insights are vital for UK patients, providing reassurance about the therapeutic benefits of sulfasalazine in chronic inflammatory conditions.
Alternative Choices
NHS prescribing alternatives with pros/cons checklist
For those considering alternatives to sulfasalazine, several medications are available through the NHS. Here’s a concise overview:
- Mesalazine: Often preferred for mild to moderate ulcerative colitis. Pros include a more targeted action and fewer side effects. Cons may include higher cost.
- Olsalazine: Effective for similar conditions, particularly UC. Pros involve fewer gastrointestinal side effects, but may not be as effective for some patients.
- Balsalazide: Additional option for ulcerative colitis treatment. Pros include a more palatable form but may carry a higher price tag.
Selecting the right medication depends on individual patient factors, including the specific condition, response to treatment, and potential side effects. Engaging in a thorough discussion with healthcare providers will help tailor a suitable therapy plan.
Understanding Sulfasalazine: Usage and Benefits
What makes sulfasalazine such a critical medication for chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis? These inflammatory disorders often bring significant pain and discomfort, leading sufferers to seek effective treatment options. Sulfasalazine, commonly marketed as Salazopyrin or Azulfidine among others, plays a vital role in managing symptoms and improving patients' quality of life.
This anti-inflammatory drug acts on the gut, primarily targeting the intestines. Health professionals often prescribe sulfasalazine to reduce inflammation, helping to control flare-ups and maintain remission in patients. Its effectiveness has been well documented, indicating that many patients experience symptom relief while on this medication.
For those considering this treatment, understanding the indications is paramount:
- Ulcerative Colitis: Acts as an intestinal anti-inflammatory agent, easing symptoms and promoting healing.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Helps in reducing joint inflammation and pain.
- Other uses: General inflammatory conditions affecting the gut.
This medication is generally well-tolerated, but like any medication, it comes with side effects and precautions that need to be understood. Regular check-ups are necessary to monitor progress and address any arising issues effectively.
Common Side Effects and Precautions with Sulfasalazine
<p Despite the benefits, patients must be aware of a range of potential side effects associated with sulfasalazine. Knowing these can lead to faster intervention if complications arise. Common side effects include:- Headaches
- Nausea and abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Rashes
Moderate side effects, while reversible in many cases, require prompt medical attention:
- Oligospermia (reversible drop in sperm count)
- Fever
- Hepatotoxicity
- Hemolytic anaemia
- Hypersensitivity reactions
For specific groups, additional precautions exist. Individuals with certain health conditions or those on specific medications should consult their healthcare provider before starting treatment:
- G6PD deficiency
- Blood dyscrasias
- Mild to moderate liver or kidney impairment
- Pregnancy (particularly in the third trimester) and breastfeeding
An essential aspect is to regularly monitor liver function and blood counts, especially when initiating treatment or when titrating doses. Such vigilance ensures any adverse reactions can be promptly managed.
Sourcing Sulfasalazine: Availability and Delivery
Accessibility is key for patients needing to manage their health. Sulfasalazine can often be sourced from local pharmacies without a prescription, enhancing its availability for those in need. Understanding the logistics around obtaining this medication can be significantly beneficial for prospective users.
Here's a look at how the delivery of sulfasalazine is structured within major cities across the UK:
| City | Region | Delivery Time |
|---|---|---|
| London | Greater London | 5–7 days |
| Birmingham | West Midlands | 5–7 days |
| Manchester | Greater Manchester | 5–7 days |
| Glasgow | Scotland | 5–7 days |
| Leeds | West Yorkshire | 5–7 days |
| Newcastle | Tyne and Wear | 5–7 days |
| Sheffield | South Yorkshire | 5–9 days |
| Bristol | South West England | 5–7 days |
| Coventry | West Midlands | 5–9 days |
| Nottingham | East Midlands | 5–9 days |
| Cardiff | Wales | 5–9 days |
| Leicester | East Midlands | 5–9 days |
By knowing where one can acquire sulfasalazine and the expected delivery times, patients can manage their treatment plans with greater ease.